Bitcoin is a peer-to-peer currency managed by a network of nodes. A node is essentially a computer that runs Bitcoin software. Bitcoin nodes send and receive transactions from other nodes in the network while also verifying their validity. Bitcoin nodes work together with Bitcoin miners to ensure the system’s integrity.
Table of Contents
- What is a node?
- Types of Bitcoin Nodes
- Why Run a Full Node?
- Consensus in the blockchain
- Maintaining Network Integrity
- Functions and Roles
- How the Network Can Shape the Future
- Conclusion
What Is a Node?

What Is a Node?
A node is any piece of hardware that connects to a larger network. For example, laptop computers connect to the internet using a Wi-Fi chip. As a result, a connected laptop can be thought of as an internet node.
By telling the node (in this case, the laptop) what data to send, receive, or keep, apps and other software let the node (in this case, the internet) function.
The Bitcoin network refers to any machine running the required software and connecting to the network as a node. Bitcoin Core, the most widely used Bitcoin software, and other programs handle the instructions that tell Bitcoin nodes to send and receive data about blocks and transactions within them.
Types of Bitcoin Nodes
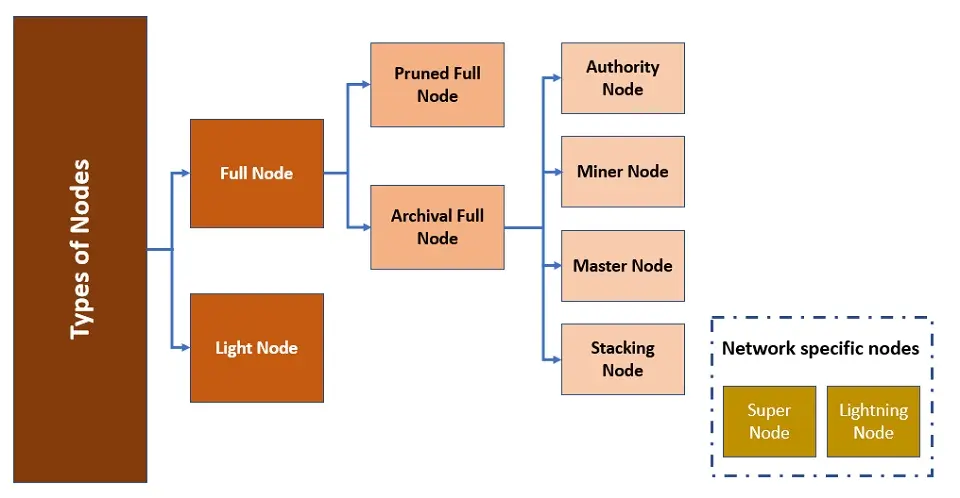
- Full Nodes
- Light Nodes
- Staking Nodes
- Master Nodes
Full Nodes
The main responsibility of a full node is to independently verify the current state of the Bitcoin coin blockchain. It accomplishes this by downloading each block and transaction from the Bitcoin blockchain, comparing them to their corresponding consensus rules, and so on. The entire node will immediately block any block or transaction that violates a Bitcoin consensus rule.
Master Nodes
Finally, master nodes are another kind of full node. Masternodes not only store the entire blockchain and validate transactions, but they also stabilize and secure their entire ecosystem and may provide services such as private transactions, instant transactions, treasury management and funding, and governance voting.

Why Run a Full Node?
There are several reasons why people run a full node for Bitcoin. Its main objective is to enable anyone to independently confirm the current status of the Bitcoin network. Consequently, a user could:
Verify the supply of bitcoin. Users can independently confirm the Bitcoin network’s current status.
Stop people from spending Bitcoin twice. A node will automatically reject any previously spent Bitcoin.
Utilize Bitcoin independently of any other parties. Rather than depending on a third party, users can broadcast and verify their transactions with a node.
To put it succinctly, Bitcoin nodes act as the network’s brain. They send, confirm, and store transactions. They transport network data to all members by acting as information superhighways and network gateways, transporting network data to all members.
Consensus in the blockchain
Consensus in a decentralized network is defined by the rules that govern the network’s operations and confirm the validity of the information contained in the blocks.
Full nodes’ primary tasks include maintaining consensus among nodes, verifying transactions, and voting proposal spots
Maintain network integrity.
To accept or relay transactions and send blocks to or from its peers, a Bitcoin node adheres to a set of consensus rules built into the Bitcoin software it runs.
Sincere Bitcoin nodes on the network keep an up-to-date copy of the blockchain and adhere to the same set of consensus guidelines. Since the blockchain is the only source of truth for the current state of every output, the network’s ability to preserve the integrity of the blockchain depends on these consensus rules.
Routing Transactions
One of the primary functions of the nodes is to route transactions. Nodes, to put it simply, facilitate the transmission of Bitcoin transactions between network users.
Your wallet software will start a transaction and broadcast it to neighbouring nodes if you want to send Bitcoin to a buddy.
Because they can independently verify every incoming transaction and store the entire blockchain database, full nodes are crucial for transaction routing. In terms of verifying and transmitting transactions, this makes them more secure than light or mining nodes.
Maintaining Blockchain Database
Bitcoin nodes maintain the blockchain database, effectively a public ledger that tracks all transactions. Complete nodes independently validate new transactions, and store, and manage an entire copy of the blockchain.
Light nodes do not maintain a perfect copy of the blockchain; instead, they depend on full nodes to view and validate transactions. Because they can’t fully verify every transaction, they are less secure, but also lighter and require fewer resources than full nodes.
Supporting Mining
Bitcoin nodes are involved in the process of generating new blocks. Specialized nodes called mining nodes assist in deriving solutions to challenging arithmetic problems and appending new blocks to the blockchain.
These nodes contribute to the integrity and security of the Bitcoin network by providing the processing power needed to verify transactions.
In order for all users to agree on which transactions are legitimate, mining is a crucial feature of Bitcoin’s consensus mechanism. Additionally, newly created bitcoins reward miners who successfully validate and add transactions to the blockchain.
A node’s chances of receiving these rewards increase with its mining power.
Providing Wallet Services
Bitcoin nodes also play an important role in wallet provisioning. Wallets are digital applications that allow users to send and receive Bitcoin, monitor balances, and manage their funds.
devices and nodes that offer wallet services serve as bridges between users’ devices and their networks.
Wallets can be both custodial and non-custodial. Custodial wallets store the user’s private keys on their behalf, whereas non-custodial wallets allow users to keep their private keys.

How the Bitcoin Network Can Shape the Future
If the Bitcoin network was critical to the widespread acceptance of cryptocurrencies, its role in the future economy will most likely be equally important.
Many people no longer carry cash or coins in their wallets, preferring to pay for goods and services with a credit card or mobile app.
These options are more convenient than carrying physical money, but they give the financial institutions that back them a lot of control, which makes some customers uncomfortable. Hacking, identity theft, and other security breaches are all issues that continue to raise consumer concerns.
Conclusion
A Bitcoin node is a member of the Bitcoin network that keeps a copy of the entire blockchain and follows protocol guidelines. Nodes play an important role in decentralization because they validate transactions and blocks, ensuring the network’s security and integrity. There are two types of nodes: full nodes, which keep the entire blockchain, and light nodes, which rely on other nodes for specific information.
